
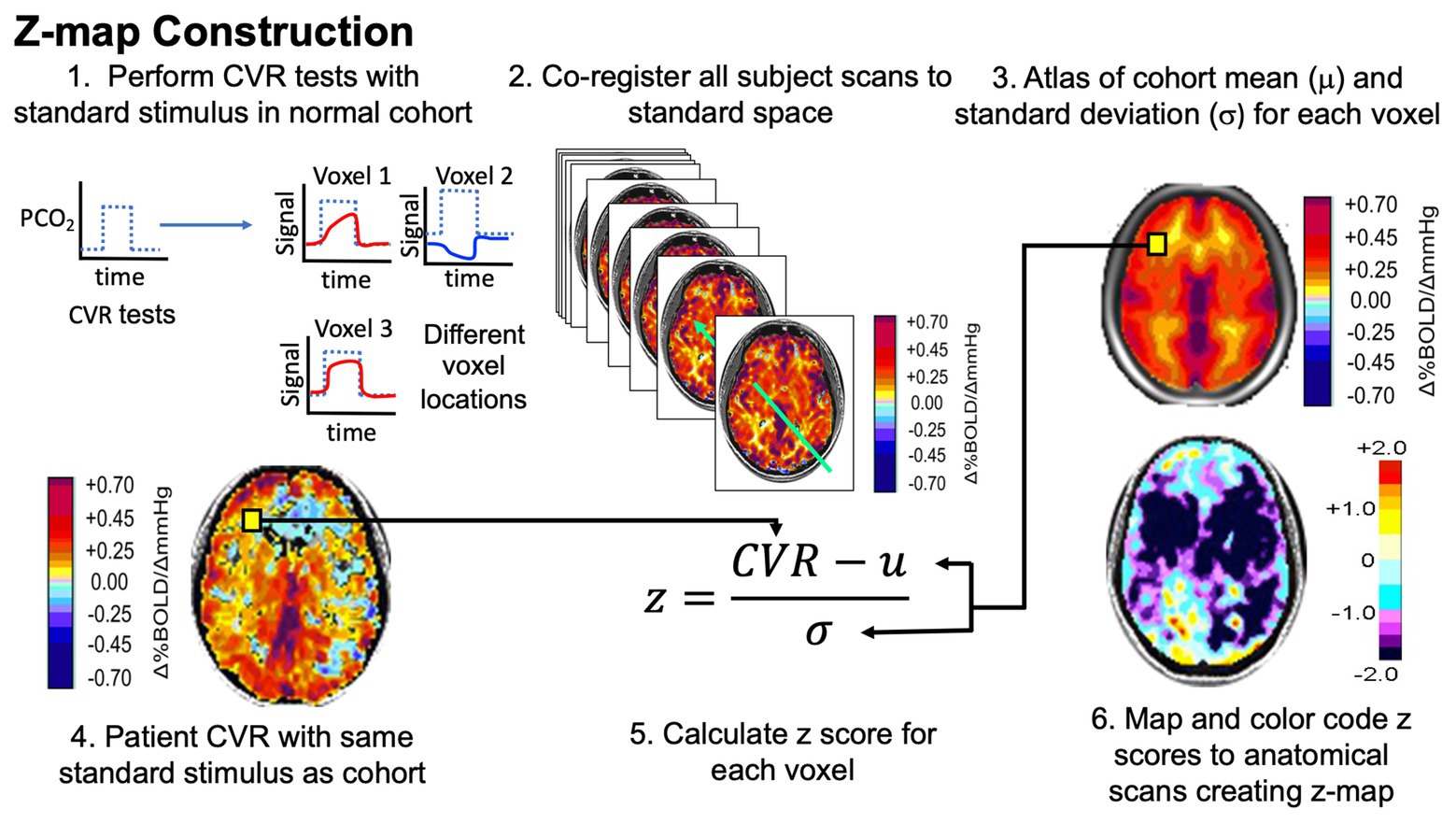
Lower CVR whole and ssCVR in the SCI-cohort was significantly (P<0.05) correlated with lower daytime blood pressure (R S≥ 0.81) and a higher frequency of hypotensive episodes (R S≥ -0.83). Neurological level of injury (NLI), modified into an ascending, continuous numeric variable, was positively correlated with GM CVR whole (R S=0.85, p=0.016), GM ssCVR (R S=0.95, p=0.001) and brainstem ssCVR (R S=0.90, p=0.006). Time since injury (TSI) displayed negative correlations with ssCVR in the GM and brainstem of SCI participants: R S=-0.77, p=0.041 and R S=-0.76, p=0.049, respectively, where R S is the Spearman’s rank Correlation Coefficient. Our results showed a longer tau in the GM of SCI participants compared to controls (median of the difference = 3.0 seconds p<0.05). A 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitor was worn to capture free-living blood pressure outcomes. In addition, CVR was further decomposed into its dynamic (tau) and static components (steady state CVR ssCVR). Initially, CVR was calculated as is standard, via the linear, least-squares fit across the whole gas challenge protocol (CVR whole). The CVR outcome measure was assessed in three ways. CVR was measured by assessing the MRI-blood oxygen level–dependent signal with hypercapnic challenge (controlled CO 2 inhalation). Thirteen participants (7 chronic SCI (all male, median age of 42 years), 6 controls (all male, median age of 33 years) were studied cross-sectionally. carbon dioxide, CO 2) or altered metabolic demand. CVR represents the capacity of brain parenchyma to change cerebral blood flow in response to a vasoactive stimulus (e.g. The aim of this study was to assess cerebrovascular reactivity (CVR) in both the grey matter (GM) and brainstem using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) in participants with SCI compared to non-injured controls. These impairments can lead to alterations in blood flow, cerebral perfusion pressure and ultimately tissue perfusion, which can lead to an elevated risk of stroke and global cognitive deficits. Subjects are being scanned on both the 1.5T MR scanner at the Edinburgh Imaging Facility WGH & the 3T MR scanner at the Edinburgh Imaging Facility RIE.Cervical and upper-thoracic spinal cord injury (SCI) commonly results in autonomic cardiovascular impairments.Finally, pulse wave analysis test & pulse wave velocity measurement are carried out using the SphygmoCor system.The subject then undergoes Doppler ultrasound in order to capture flow measurements of the internal & common carotid arteries.
Cerebrovascular reactivity definition plus#
The subject also undergoes structural imaging, plus flow sensitive scans of the cerebral aqueduct, venous sinuses & carotid arteries.Blood Oxygen Level Dependent (BOLD) sequences allow measurement of the CVR.MR allows measurement of CVR in grey matter, white matter, & in white matter hyperintensities.During the MR scan which follows, the subject undergoes hypercapnia again.Retinal imaging allows measurement of retinal vascular reactivity & can be correlated with CVR.Prior to MR scanning, the subject undergoes retinal imaging, both before & after the induced hypercapnia.Determine sample size requirements prior to phase 2 trials & mechanistic studies.Determine feasibility & to compare CVR with retinal vasoreactivity & measures of peripheral vascular health.Patient data pertaining to CVR is currently limited.To determine if various imaging methods are sensitive & practical enough to use in early phase clinical trials of interventions to prevent progressive small vessel disease.It is a well-documented method of measuring CVR.Inhaling this mixture induces hypercapnia & causes vasodilation.CVR requires a subject to inhale a mixture of air & carbon dioxide.Cerebrovascular reactivity is the change in cerebral blood flow in response to a vaso-active stimulus.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
